TIPS FOR CHOOSING AUTHENTIC AND HIGH QUALITY CORDYCEPS SUPPLEMENTS
Cordyceps Health Support Role (1)
Cordyceps is a parasitic fungus on the larval body of insects living on steep mountainous terrain. Therefore, they are challenging to exploit and have a high cost. It is also one of the rare fungis that have been used in Traditional Chinese Medicine for centuries to treat fatigue, sickness, and kidney health and to help improve low libido.
Cordyceps supplements and products are becoming increasingly popular, known for their many health benefits:
- Increase exercise performance
- Anti-aging
- Potential anti-tumor effects
- Help manage type 2 diabetes
- Benefits with cardiovascular health
- May help reduce inflammation
Photo: Cordyceps sinensis
The alarming situation of the origin and quality of Cordyceps in the Vietnam market (2)
As a valuable medicinal fungi for health and with high economic value, the Cordyceps products business in Vietnam is currently floating. It has many systematic problems regarding price, product origin, and quality.
According to VOV – Voice of Vietnam radio, naturally grown cordyceps are mainly exploited in Tibet, Bhutan, and some provinces in China such as Sichuan, Gansu, and Yunnan. The annual quantity is less than one quintal, which is very scarce, so the price is exceptionally high. On online sales sites, each kilogram of dried cordyceps is for sale for up to a billion dong.
Currently, a few countries such as China, Korea, Japan, and Vietnam have successfully researched and artificially cultured cordyceps. The low price of cultured cordyceps is only 1/10, even 1/100, compared to imported goods advertised as wild exploitation.
Not only the imported cordyceps but also refined products in Vietnam challenge the customers when Cordyceps are sold up t the price of 10-20 million VND/kg. On the contrary, some people are selling Cordyceps at the cost of a few million VND/kg. . Besides, the content in the advertised cordyceps product also shows that the market is still quite messy.
Therefore, before choosing a health supplement product extracted from Cordyceps, consumers need to know the ingredients and quality standards of this precious medicinal fungi.
Photo: Goods of unknown origin were seized by authorities.
Standards for quality assessment of Cordyceps in Modern Medicine
Based on the external appearance of Cordyceps:
To avoid confusion with fake Cordyceps made from powder or similar medicinal fungi, consumers need to recognize the distinctive characteristics of this medicinal fungi:
- Cordyceps consists of a 2.5-3 cm long and 3-5 mm in diameter larva. (6)
- The head of the larva grows into a cylindrical stroma. The stroma is usually 3-6cm long and can be up to 11cm long. The bottom of the stroma has a diameter of 1.5-4mm; the top is bulging and tapered. The whole part is 10-45mm long and 2.5-6mm in diameter. If cordyceps is young, the body is solid. When it is old, the body is hollow. When looking under the microscope, you can see the enlarged part with a rough shell. (6)
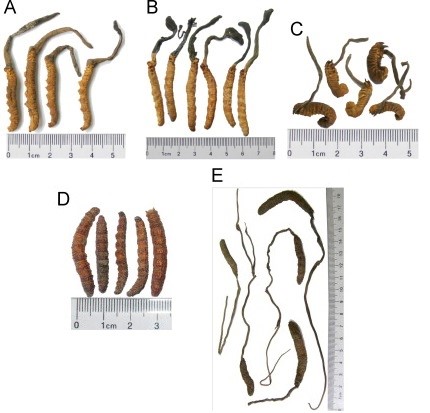
Comparison of commonly used Cordyceps sinensis with similar parasitic fungi: (7)
- A – Cordyceps sinensis: larva body with 8 pairs of feet on the abdomen, 4 pairs apparent in the center; stroma with sterile acuminate apex.
- B – Cordyceps gunnii: larva body with 8 pairs of feet on the abdomen, indistinct; stroma stout and rough, with sterile bulgy or branched apex.
- C – Cordyceps barnesii: larva body curved kidney-shaped; head small, with a pair of teeth.
- D – Cordyceps gracilis: larva body with 20–40 annulations,. usually without stroma.
- E – Cordyceps liangshanensis: feet indistinct; Stroma thread-like, 10–30 cm in length.
Photo: Cordyceps sinensis and its similar parasitic fungi species.
Based on the active ingredients of the medicinal plant:
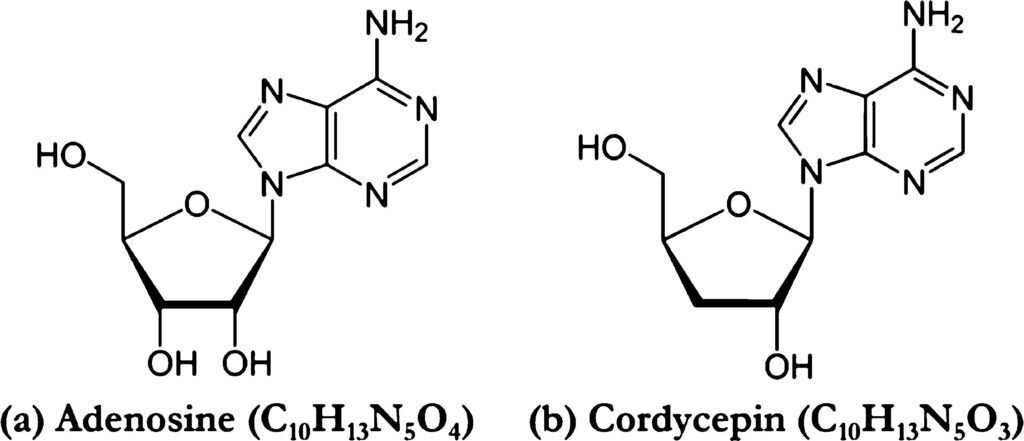
Not only is it a long-standing medicinal ingredient of Traditional Oriental Medicine, but in modern medicine, Cordyceps also contains many valuable active ingredients such as: Cordycepin, Adenosine, protein, fat, essential amino acids. In addition, this medicinal herb also contains many vitamins (B1, B2, B12, E, and K) and minerals (iron, calcium, magnesium, and zinc). (3)
The most prominent are the two active Nucleosides ingredients: Adenosine and Cordycepin:
- Adenosine helps improve sleep quality, improves blood circulation to the heart, and prevents the formation of blood clots and myocardial ischemia. (4)
- Cordycepin has anti-cancer, and anti-microbial effects; prevents cancer cells from metastasizing or regenerating, supports the treatment of intestinal diseases; prevents type 2 diabetes genes from developing, and supports the treatment of diabetes. (4)
To date, nucleosides are believed to be the active components in Cordyceps, and Adenosine has been used as marker for quality control of Cordyceps sinensis.
Photo: Adenosine and Cordycepin
Be an intelligent consumer in choosing Cordyceps supplement products!
As a precious medicinal fungus that has been used for a long time and has many health benefits, the current supply of Cordyceps is still not strictly regulated in the Vietnam market. There are many health care products made from Cordyceps in circulation with different prices and quality that are challenging for consumers to choose from.
Therefore, to choose high-quality products and ensure safety and effectiveness, consumers need to understand the identification characteristics of authentic Cordyceps. Consider purchasing products from branded and reliable manufacturers, and must have strict standards of the content. Last but not least, Adenosine is the crucial marker in evaluating the quality of this medicinal fungus.
Source:
(1) https://www.vinmec.com/vi/tin-tuc/thong-tin-suc-khoe/dinh-duong/6-loi-ich-cua-dong-trung-ha-thao-dua-tren-khoa-hoc/?link_type=related_posts
(2) https://vietnamnet.vn/thi-truong-dong-trung-ha-thao-loan-gia-chat-luong-bi-tha-noi-757727.html
(3) Syed Amir Ashraf et al. Cordycepin for Health and Wellbeing: A Potent Bioactive Metabolite of an Entomopathogenic Medicinal Fungus Cordyceps with Its Nutraceutical and Therapeutic Potential. Molecules. 2020 Jun; 25(12): 2735
(4) https://bvnguyentriphuong.com.vn/y-hoc-co-truyen/adenosine-trong-dong-trung-ha-thao
(5) S.P. Li, F.Q. Yang, Karl W.K. Tsim: Quality control of Cordyceps sinensis, a valued traditional Chinese medicine. Journal of Pharmaceutical and Biomedical Analysis 41 (2006) 1571–1584.
(6) Đỗ Tất Lợi (2004). Những cây thuốc và vị thuốc Việt Nam, xuất bản lần XII, NXB Y Học, 882.
(7) Liu, Hui-juan & Hu, Hao-bin & Chu, Chu & Li, Qin & Li, Ping. (2011). Morphological and microscopic identification studies of Cordyceps and its counterfeits. Acta Pharmaceutica Sinica B. 1. 189–195. 10.1016/j.apsb.2011.06.013.
- 1. THE EXPERT’S SHARING: THE KEY TO START A NEW DAY FULL OF ENERGY
- 2. GINSENG – “SPECIAL” HERBAL MEDICINE FOR FATIGUE PEOPLE
- 3. THE ROLE OF HERBAL IN INCREASING PHYSICAL & MENTAL HEALTH
- 4. LIST OF 3 EFFECTIVE BRAIN SUPPLEMENT HERBALS
- 5. FATIGUE – WARNING SIGNS OF CHRONIC FATIGUE SYNDROM, YOU SHOULD KNOW?
- 6. ADVICE FROM THE PROFESSIONAL ABOUT “STRENGTHEN RESISTANCE IN THE TIME OF COVID”