7 Proven Health Benefits of Ginseng
Ginseng has been used in traditional Chinese medicine for centuries.
This slow-growing, short plant with fleshy roots can be classified three ways, depending on how long it is grown: fresh, white or red.
Fresh ginseng is harvested before 4 years, while white ginseng is harvested between 4–6 years and red ginseng is harvested after 6 or more years.

There are many types of this herb, but the most popular are American ginseng (Panax quinquefolius) and Asian ginseng (Panax ginseng).
American and Asian ginseng vary in their concentration of active compounds and effects on the body. It is believed that American ginseng works as a relaxing agent, whereas the Asian variety has an invigorating effect (1),(2).
Ginseng contains two significant compounds: ginsenosides and gintonin. These compounds complement one another to provide health benefits (3).
Here are 7 evidence-based health benefits of ginseng
1. Potent Antioxidant That May Reduce Inflammation
Ginseng has beneficial antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties (4).
Some test-tube studies have shown that ginseng extracts and ginsenoside compounds could inhibit inflammation and increase antioxidant capacity in cells (5),(6).
For example, one test-tube study found that Korean red ginseng extract reduced inflammation and improved antioxidant activity is skin cells from people with eczema (7).
The results are promising in humans, as well.
A study followed 71 postmenopausal women who took 3 grams of red ginseng or a placebo daily for 12 weeks. Antioxidant activity and oxidative stress markers were then measured.
Researchers concluded that red ginseng may help reduce oxidative stress by increasing antioxidant enzyme activities (8).
SUMMARY: Ginseng has been shown to help reduce inflammatory markers and help protect against oxidative stress.
2. May Benefit Brain Function
Ginseng could help improve brain functions like memory, behavior and mood (9),(10).
Some test-tube and animal studies show that components in ginseng, like ginsenosides and compound K, could protect the brain against damage caused by free radicals (11),(12),(13).
Another study examined how single doses of either 200 or 400 mg of Panax ginseng affected mental performance, mental fatigue and blood sugar levels in 30 healthy adults before and after a 10-minute mental test.
The 200-mg dose, as opposed to the 400-mg dose, was more effective at improving mental performance and fatigue during the test (14).
It is possible that ginseng assisted the uptake of blood sugar by cells, which could have enhanced performance and reduced mental fatigue. Yet it is not clear why the lower dose was more effective than the higher one.
What’s more, other studies found positive effects on brain function and behavior in people with Alzheimer’s disease (15),(16),(17).
SUMMARY: Ginseng has been shown to benefit mental functions, feelings of calmness and mood in both healthy people and those with Alzheimer’s disease.
3. Could Improve Erectile Dysfunction
Research has shown that ginseng may be a useful alternative for the treatment of erectile dysfunction (ED) in men (18),(19).
It seems that compounds in it may protect against oxidative stress in blood vessels and tissues in the penis and help restore normal function (20),(21).
Additionally, studies have shown that ginseng may promote the production of nitric oxide, a compound that improves muscle relaxation in the penis and increases blood circulation (21),(22).
One study found that men treated with Korean red ginseng had a 60% improvement in ED symptoms, compared to 30% improvement produced by a medication used to treat ED (23).
However, more studies are needed to draw definite conclusions about the effects of ginseng on ED.
SUMMARY: Ginseng may improve symptoms of erectile dysfunction by decreasing oxidative stress in tissues and enhancing blood flow in penile muscles.
4. May Boost the Immune System
Ginseng may strengthen the immune system.
Some studies exploring its effects on the immune system have focused on cancer patients undergoing surgery or chemotherapy treatment.
One study followed 39 people who were recovering from surgery for stomach cancer, treating them with 5,400 mg of ginseng daily for two years.
Interestingly, these people had significant improvements in immune functions and a lower recurrence of symptoms.
It seems that ginseng extract could enhance the effect of vaccinations against diseases like influenza, as well (24).
Even though these studies show improvements in immune system markers in people with cancer, more research is needed to demonstrate the efficacy of ginseng in boosting resistance to infections in healthy people (25).
SUMMARY: Ginseng may strengthen the immune system in people with cancer and even enhance the effects of certain vaccinations.
5. May Have Potential Benefits Against Cancer
Ginseng may be helpful in reducing the risk of certain cancers (26).
Ginsenosides in this herb have been shown to help reduce inflammation and provide antioxidant protection (27),(28).
The cell cycle is the process by which cells normally grow and divide. Ginsenosides could benefit this cycle by preventing abnormal cell production and growth (27),(28).
A review of several studies concluded that people who take ginseng may have a a 16% lower risk of developing cancer (27) .
Moreover, an observational study suggested that people taking ginseng could be less likely to develop certain types of cancer, such as lip, mouth, esophagus, stomach, colon, liver and lung cancer, than those who do not take it (29).
Ginseng may also help improve the health of patients undergoing chemotherapy, reduce side effects and enhance the effect of some treatment drugs (28).
While studies on the role of ginseng in cancer prevention show some benefits, they remain inconclusive (30).
SUMMARY: Ginsenosides in ginseng seem to regulate inflammation, provide antioxidant protection and maintain the health of cells, which could help decrease the risk of certain kinds of cancer. Nevertheless, more research is needed.
6. May Fight Tiredness and Increase Energy Levels
Ginseng has been shown to help fight fatigue and promote energy.
Various animal studies have linked some components in ginseng, like polysaccharides and oligopeptides, with lower oxidative stress and higher energy production in cells, which could help fight fatigue (31),(32),(33).
One four-week study explored the effects of giving 1 or 2 grams of Panax ginseng or a placebo to 90 people with chronic fatigue.
Those given Panax ginseng experienced less physical and mental fatigue, as well as reductions in oxidative stress, than those taking the placebo (34).
Furthermore, a review of over 155 studies suggested that ginseng supplements may not only help reduce fatigue but also enhance physical activity (35).
SUMMARY: Ginseng may help fight fatigue and enhance physical activity by lowering oxidative damage and increasing energy production in cells.
7. Could Lower Blood Sugar
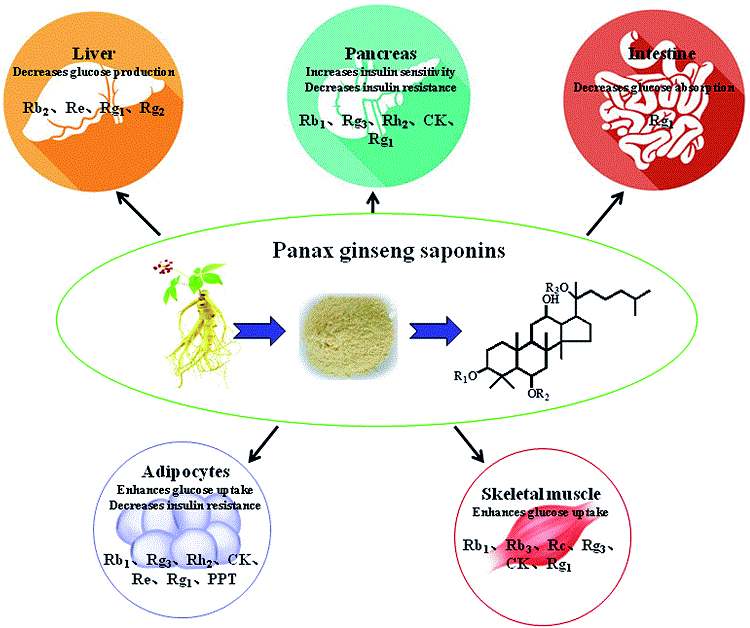
Ginseng seems to be beneficial in the control of blood glucose in people both with and without diabetes (36),(37).
American and Asian ginseng have been shown to improve pancreatic cell function, boost insulin production and enhance the uptake of blood sugar in tissues (36).
Moreover, studies show that ginseng extracts help by providing antioxidant protection that reduce free radicals in the cells of those with diabetes (36).
One study assessed the effects of 6 grams of Korean red ginseng, along with the usual anti-diabetic medication or diet, in 19 people with type 2 diabetes.
Interestingly, they were able to maintain good blood sugar control throughout the 12-week study. They also had an 11% decrease in blood sugar levels, a 38% decrease in fasting insulin and a 33% increase in insulin sensitivity (38).
It seems that fermented red ginseng could be even more effective at blood sugar control. Fermented ginseng is produced with the help of live bacteria that transform the ginsenosides into a more easily absorbed and potent form (39).
In fact, a study demonstrated that taking 2.7 grams of fermented red ginseng daily was effective at lowering blood sugar and increasing insulin levels after a test meal, compared to a placebo (40).
SUMMARY: Ginseng, particularly fermented red ginseng, may help increase insulin production, enhance blood sugar uptake in cells and provide antioxidant protection.
Easy to Add to Your Diet
Ginseng root can be consumed in many ways. It can be eaten raw or you can lightly steam it to soften it.
It can also be stewed in water to make a tea. To do this, just add hot water to freshly sliced ginseng and let it steep for several minutes.
Ginseng can be added to various recipes like soups and stir-frys, too. And the extract can be found in powder, tablet, capsule and oil forms.
How much you should take depends on the condition you want to improve. Overall, daily doses of 1–2 grams of raw ginseng root or 200–400 mg of extract are suggested. It’s best to start with lower doses and increase over time.
Look for a standard ginseng extract that contains 2–3% total ginsenosides, and consume it before meals to increase absorption and get the full benefits.
SUMMARY: Ginseng can be eaten raw, made into tea or added to various dishes. It can also be consumed as a powder, capsule or oil.
Safety and Potential Side Effects
According to research, ginseng appears to be safe and should not produce any serious adverse effects.
However, people taking diabetes medications should monitor their blood sugar levels closely when using ginseng to ensure these levels do not go too low.
Additionally, ginseng may reduce the effectiveness of anticoagulant drugs.
For these reasons, talk to your doctor before supplementing with it.
Note that due to the lack of safety studies, ginseng is not recommended for children or women who are pregnant or breastfeeding.
SUMMARY: While ginseng appears to be safe, people taking certain medications should pay attention to possible drug interactions.
The Bottom Line
Ginseng is an herbal supplement that has been used for centuries in Chinese medicine.
It is commonly touted for its antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects. It could also help regulate blood sugar levels and have benefits for some cancers.
What’s more, ginseng may strengthen the immune system, enhance brain function, fight fatigue and improve symptoms of erectile dysfunction.
Ginseng can be consumed raw or lightly steamed. It can also easily be added to your diet via its extract, capsule or powder form.
Whether you want to improve a certain condition or simply give your health a boost, ginseng is definitely worth a try.
Written by Arlene Semeco, MS, RD on February 28, 2018
Reference:
Yin and Yang of ginseng pharmacology: ginsenosides vs gintonin
Dong-soon Im, Seung-yeol Nah – Acta Pharmacol Sin 2013 Nov; 34(11):1367-73.
Chemical Diversity of Panax ginseng, Panax quinquifolium, and Panax notoginseng
Dong-Hyun Kim – J Ginseng Res 2012 Jan; 36(1):1-15
Efficacy comparison of Korean ginseng and American ginseng on body temperature and metabolic parameters
Eun-Young Park, Mi-Hwi Kim, Eung-Hwi Kim, Eun-Kyu Lee, In-Sun Park, Duck-Choon Yang, Hee-Sook Jun – Am J Chin Med 2014; 42(1):173-87
Red ginseng abrogates oxidative stress via mitochondria protection mediated by LKB1-AMPK pathway
Guang-Zhi Dong, Eun Jeong Jang, Seung Ho Kang, Il Je Cho, Sun-Dong Park, Sang Chan Kim, Young Woo Kim – BMC Complement Altern Med 2013 Mar 18; 13:64
Effects of Panax ginseng on tumor necrosis factor-α-mediated inflammation: a mini-review
Davy C W Lee, Allan S Y Lau – Molecules 2011 Mar 30; 16(4):2802-16
Potentiation of antioxidative and anti-inflammatory properties of cultured wild ginseng root extract through probiotic fermentation
Byoung-Gun Park, Hyun-Joo Jung, Young-Wook Cho, Hye-Won Lim, Chang-Jin Lim – J Pharm Pharmacol 2013 Mar; 65(3):457-64
Anti-inflammatory and Anti-oxidative Effects of Korean Red Ginseng Extract in Human Keratinocytes
Chang-Eui Hong, Su-Yun Lyu – Immune Netw 2011 Feb; 11(1):42-9
Antioxidative effects of Korean red ginseng in postmenopausal women: a double-blind randomized controlled trial
Seok Kyo Seo, Yeon Hong, Bo Hyon Yun, Seung Joo Chon, Yeon Soo Jung, Joo Hyun Park, SiHyun Cho, Young Sik Choi, Byung Seok Lee – J Ethnopharmacol 2014 Jul 3; 154(3):753-7
Ginseng for cognition
Jinsong Geng, Jiancheng Dong, Hengjian Ni, Myeong Soo Lee, Taixiang Wu, Kui Jiang, Guohua Wang, Ai Ling Zhou, Reem Malouf – Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2010 Dec 8; (12):CD007769
Ginseng for health care: a systematic review of randomized controlled trials in Korean literature
Jiae Choi, Tae-Hun Kim, Tae-Young Choi, Myeong Soo Lee – PLoS One 2013; 8(4):e59978
Compound K derived from ginseng: neuroprotection and cognitive improvement
Jisun Oh, Jong-Sang Kim – Food Funct 2016 Nov 9; 7(11):4506-4515
Effects and mechanisms of ginseng and ginsenosides on cognition
Imogen Smith, Elizabeth M Williamson, Sophie Putnam, Jonathan Farrimond, Benjamin J Whalley – Nutr Rev 2014 May; 72(5):319-33
Neuroprotective effects of ginsenosides
Wolf-Dieter Rausch, Shu Liu, Gabriele Gille, Khaled Radad – Acta Neurobiol Exp (Wars) 2006; 66(4):369-75
Single doses of Panax ginseng (G115) reduce blood glucose levels and improve cognitive performance during sustained mental activity
Jonathon L Reay, David O Kennedy, Andrew B Scholey – J Psychopharmacol 2005 Jul; 19(4):357-65
An open-label trial of Korean red ginseng as an adjuvant treatment for cognitive impairment in patients with Alzheimer’s disease
J-H Heo, S-T Lee, K Chu, M J Oh, H-J Park, J-Y Shim, M Kim – Eur J Neurol 2008 Aug; 15(8):865-8
Heat-processed ginseng enhances the cognitive function in patients with moderately severe Alzheimer’s disease
Jae-Hyeok Heo, Soon-Tae Lee, Kon Chu, Min Jung Oh, Hyun-Jung Park, Ji-Young Shim, Manho Kim – Nutr Neurosci 2012 Nov; 15(6):278-82
Improvement of cognitive deficit in Alzheimer’s disease patients by long term treatment with korean red ginseng
Jae-Hyeok Heo, Soon-Tae Lee, Min Jung Oh, Hyun-Jung Park, Ji-Young Shim, Kon Chu, Manho Kim – J Ginseng Res 2011 Nov; 35(4):457-61
A double-blind crossover study evaluating the efficacy of korean red ginseng in patients with erectile dysfunction: a preliminary report
Bumsik Hong, Young Hwan Ji, Jun Hyuk Hong, Ki Yeul Nam, Tai Young Ahn – J Urol 2002 Nov; 168(5):2070-3
Study of the efficacy of Korean Red Ginseng in the treatment of erectile dysfunction
Enrico de Andrade, Alexandre A de Mesquita, Joaquim de Almeida Claro, Priscila M de Andrade, Valdemar Ortiz, Mário Paranhos, Miguel Srougi – Asian J Androl 2007 Mar; 9(2):241-4
Panax notoginseng saponins improve erectile function through attenuation of oxidative stress, restoration of Akt activity and protection of endothelial and smooth muscle cells in diabetic rats with erectile dysfunction
Huan Li, Wei-Yang He, Fan Lin, Xin Gou – Urol Int 2014;93(1):92-9
Red ginseng for treating erectile dysfunction: a systematic review
Dai-Ja Jang, Myeong Soo Lee, Byung-Cheul Shin, Young-Cheoul Lee, Edzard Ernst – Br J Clin Pharmacol 2008 Oct;66(4):444-50
Nutrients and botanicals for erectile dysfunction: examining the evidence
Douglas McKay – Altern Med Rev 2004 Mar;9(1):4-16
Clinical efficacy of Korean red ginseng for erectile dysfunction
H K Choi, D H Seong, K H Rha – Int J Impot Res 1995 Sep;7(3):181-6
Efficacy and safety of the standardised Ginseng extract G115 for potentiating vaccination against the influenza syndrome and protection against the common cold [corrected]
F Scaglione, G Cattaneo, M Alessandria, R Cogo – Drugs Exp Clin Res 1996; 22(2):65-72
Immune system effects of echinacea, ginseng, and astragalus: a review
Keith I Block 1, Mark N Mead – Integr Cancer Ther 2003 Sep;2(3):247-67
Red ginseng and cancer treatment
Chong-Zhi Wang, Samantha Anderson, Wei DU, Tong-Chuan He, Chun-Su Yuan – Chin J Nat Med 2016 Jan; 14(1):7-16
Ginseng consumption and risk of cancer: A meta-analysis
Xin Jin, Dao-Biao Che, Zhen-Hai Zhang, Hong-Mei Yan, Zeng-Yong Jia, Xiao-Bin Jia – J Ginseng Res 2016 Jul; 40(3):269-77
Recent advances in ginseng as cancer therapeutics: a functional and mechanistic overview
Alice S T Wong, Chi-Ming Che, Kar-Wah Leung – Nat Prod Rep 2015 Feb; 32(2):256-72
Preventive effect of ginseng intake against various human cancers: a case-control study on 1987 pairs
T K Yun, S Y Choi – Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 1995 Jun; 4(4):401-8
Ginseng and cancer
Ahmet Unlu, Erdinc Nayir, Onder Kirca, Hale Ay, Mustafa Ozdogan – J BUON Nov-Dec 2016; 21(6):1383-1387
The effective mechanism of the polysaccharides from Panax ginseng on chronic fatigue syndrome
Jia Wang, Chengxin Sun, Yan Zheng, Hongling Pan, Yifa Zhou, Yuying Fan – Arch Pharm Res 2014 Apr; 37(4):530-8.
Anti-fatigue activity of the water-soluble polysaccharides isolated from Panax ginseng C. A. Meyer
Jia Wang, Shanshan Li, Yuying Fan, Yan Chen, Dan Liu, Hairong Cheng, Xiaoge Gao, Yifa Zhou – J Ethnopharmacol 2010 Jul 20; 130(2):421-3
Anti-Fatigue Effects of Small Molecule Oligopeptides Isolated from Panax ginseng C. A. Meyer in Mice
Lei Bao, Xiaxia Cai, Junbo Wang, Yuan Zhang, Bin Sun, Yong Li – Nutrients 2016 Dec 13; 8(12):807
Antifatigue effects of Panax ginseng C.A. Meyer: a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial
Hyeong-Geug Kim, Jung-Hyo Cho, Sa-Ra Yoo, Jin-Seok Lee, Jong-Min Han, Nam-Hun Lee, Yo-Chan Ahn, Chang-Gue Son – PLoS One 2013 Apr 17; 8(4):e61271
Efficacy of Ginseng Supplements on Fatigue and Physical Performance: a Meta-analysis
Hoang Viet Bach, Jeongseon Kim, Seung Kwon Myung, Young Ae Cho – J Korean Med Sci 2016 Dec; 31(12):1879-1886
Ginseng on hyperglycemia: effects and mechanisms
John Zeqi Luo, Luguang Luo – Evid Based Complement Alternat Med 2009 Dec; 6(4):423-7
The effect of ginseng (the genus panax) on glycemic control: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled clinical trials
Esra’ Shishtar, John L Sievenpiper, Vladimir Djedovic, Adrian I Cozma, Vanessa Ha, Viranda H Jayalath, David J A Jenkins, Sonia Blanco Meija, Russell J de Souza, Elena Jovanovski, Vladimir Vuksan – PLoS One 2014 Sep 29; 9(9):e107391
Korea red ginseng (Panax ginseng) improves glucose and insulin regulation in well-controlled, type 2 diabetes: result of a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study of efficacy and safety
Vladimir Vuksan, Mi-Kyung Sung, John L Sievenpiper, P Mark Stavro, Alexandra L Jenkins, Marco Di Buono, Kwang-Seung Lee, Lawrence A Leiter, Ki Yeul Nam, John T Arnason, Melody Choi, Asima Naeem – Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis 2008 Jan; 18(1):46-56
Bifidus fermentation increases hypolipidemic and hypoglycemic effect of red ginseng
Hien-Trung Trinh 1, Sang-Jun Han, Sang-Wook Kim, Young Chul Lee, Dong-Hyun Kim – J Microbiol Biotechnol 2007 Jul; 17(7):1127-33
Postprandial glucose-lowering effects of fermented red ginseng in subjects with impaired fasting glucose or type 2 diabetes: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial
Mi-Ra Oh, Soo-Hyun Park, Sun-Young Kim, Hyang-Im Back, Min-Gul Kim, Ji-Young Jeon, Ki-Chan Ha, Won-Taek Na, Youn-Soo Cha, Byung-Hyun Park, Tae-sun Park 1, Soo-Wan Chae – BMC Complement Altern Med 2014 Jul 11;14:237
- 1. Energize and focus your new year with Ginseng and Ginkgo Biloba
- 2. CAN PEOPLE WITH HYPERTENSION USE CORDYCEPS?
- 3. COMMON HABITS CAUSES CEREBRAL ISCHEMIA
- 4. TIPS FOR STAYING HEALTHY IN THE AUTUMN
- 5. THE EXPERT’S SHARING: THE KEY TO START A NEW DAY FULL OF ENERGY
- 6. GINSENG – “SPECIAL” HERBAL MEDICINE FOR FATIGUE PEOPLE

